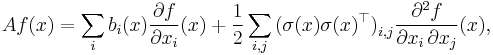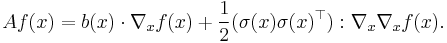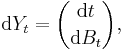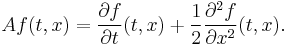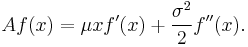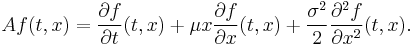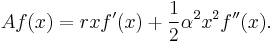Infinitesimal generator (stochastic processes)
In mathematics — specifically, in stochastic analysis — the infinitesimal generator of a stochastic process is a partial differential operator that encodes a great deal of information about the process. The generator is used in evolution equations such as the Kolmogorov backward equation (which describes the evolution of statistics of the process); its L2 Hermitian adjoint is used in evolution equations such as the Fokker-Planck equation (which describes the evolution of the probability density functions of the process).
Contents |
Definition
Let X : [0, +∞) × Ω → Rn defined on a probability space (Ω, Σ, P) be an Itô diffusion satisfying a stochastic differential equation of the form
where B is an m-dimensional Brownian motion and b : Rn → Rn and σ : Rn → Rn×m are the drift and diffusion fields respectively. For a point x ∈ Rn, let Px denote the law of X given initial datum X0 = x, and let Ex denote expectation with respect to Px.
The infinitesimal generator of X is the operator A, which is defined to act on suitable functions f : Rn → R by
The set of all functions f for which this limit exists at a point x is denoted DA(x), while DA denotes the set of all f for which the limit exists for all x ∈ Rn. One can show that any compactly-supported C2 (twice differentiable with continuous second derivative) function f lies in DA and that
or, in terms of the gradient and scalar and Frobenius inner products,
Generators of some common processes
- Standard Brownian motion on Rn, which satisfies the stochastic differential equation dXt = dBt, has generator ½Δ, where Δ denotes the Laplace operator.
- The two-dimensional process Y satisfying
- where B is a one-dimensional Brownian motion, can be thought of as the graph of that Brownian motion, and has generator
- The Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process on R, which satisfies the stochastic differential equation dXt = μXt dt + σ dBt, has generator
- Similarly, the graph of the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process has generator
- A geometric Brownian motion on R, which satisfies the stochastic differential equation dXt = rXt dt + αXt dBt, has generator
See also
References
- Øksendal, Bernt K. (2003). Stochastic Differential Equations: An Introduction with Applications (Sixth ed.). Berlin: Springer. ISBN 3-540-04758-1. (See Section 7.3)
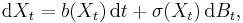
![A f (x) = \lim_{t \downarrow 0} \frac{\mathbf{E}^{x} [f(X_{t})] - f(x)}{t}.](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/d693bd60e4410eea2df6657885c9a5fc.png)